Certification
Syllabus¶
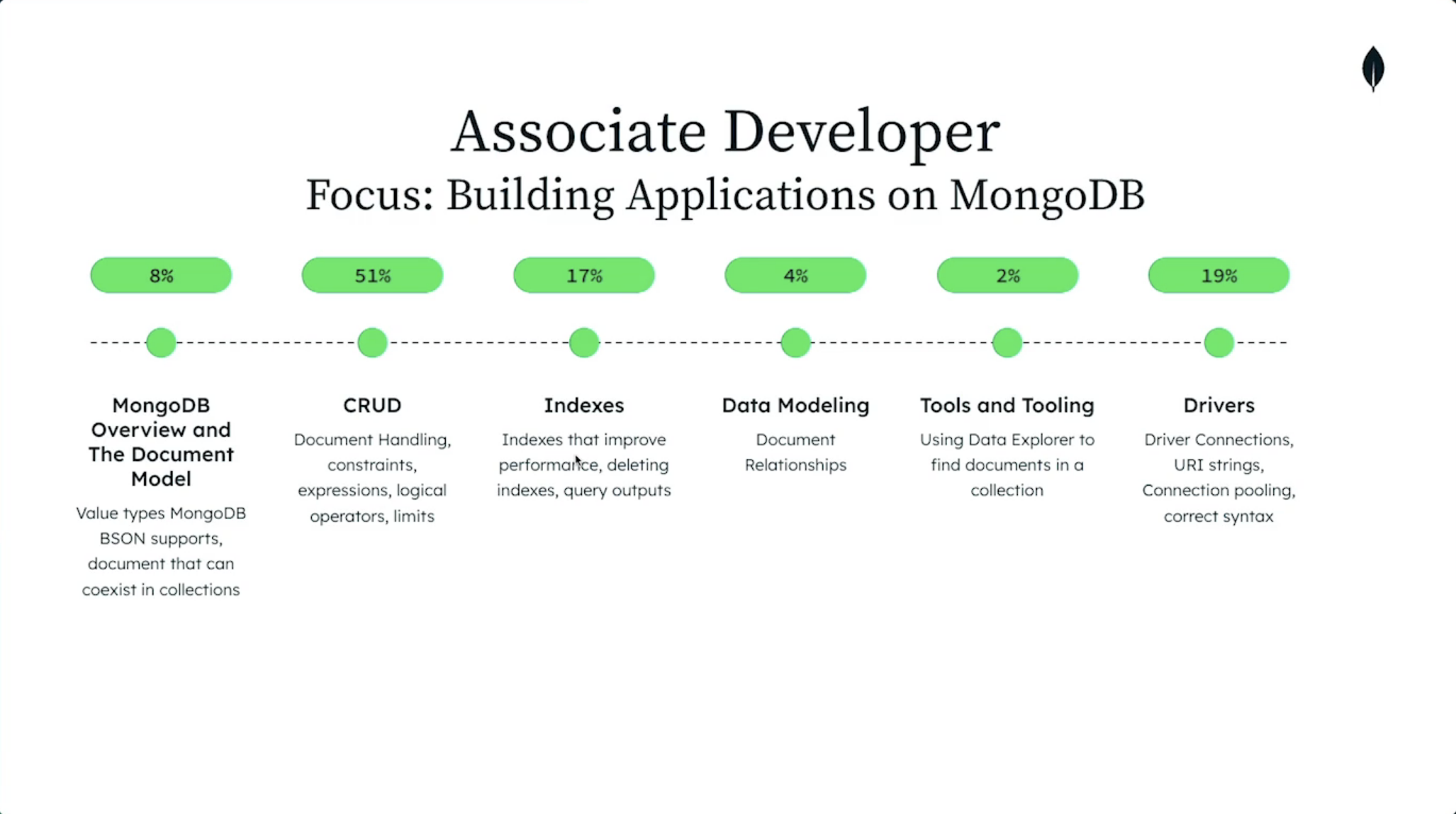
MongoDB overview¶
- Understand Database, Collections and Documents
- MongoDB stores data records as BSON documents
- BSON is a binary representation of JSON documents
Sample Scenario: Given a set of documents, identify what documents can co-exist in a collection
CRUD¶
Insert Methods:¶
- db.collection.insertOne()
- db.collection.insertMany()
- db.collection.bulkWrite()
Identify properly formed insert statements
Read Method:¶
- db.collection.find(query, projection, options)
- Use of Comparison, Logical, Element and Array query and projection operators
- Common curson methods: sort, limit0), count, and skip()
Sample Scenario: Identify projection in a query like: db.product.find( { type: "A" ), { item: 1, color: 1 })
Update Methods:¶
db.collection.updateOne(<filter>, <update>, <options>)db.collection.updateMany(<filter>, <update>, <options>)db.collection.replaceOne(<filter>, <update>, <options>)
Additional Update Methods:
db.collection.updateOne(<filter>, <update>, <options>)db.collection.findOneAndReplace()db.collection.findOneAndUpdate()db.collection.findAndModify()
Update Operators: $set, $inc, Sunset, $max
Array Update Operators and Upsert
Delete Methods:¶
- db.collection.deleteMany()
- db.collection.deleteOne()
- findOneAndDelete()
- db.collection.remove()
Build query filters
Sample Scenario: Identify a delete expression to remove a given document from a collection
Aggregation:¶
Aggregation pipeline consists of one or more stages that process documents
Create an aggregation pipeline using db.collection.aggregate() method
Build an aggregation pipeline using $match, $group, $sort, $project, etc
Sample Scenario: Identify the output of an aggregation expression
Indexes¶
Why use Indexes in MongoDB?
Types of Indexes offered by MongoDB
Methods to manage indexes: - db.collection.createIndex() - db.collection.getIndexes() - db.collection.dropIndex()
Limitations of using Indexes
Sample Scenario: Understand the Explain result and information on query plans and execution statistics of the query plans
Data Modeling¶
Flexible Schema
Data Model Design: - Embedded Data Models - Normalized Data Models
Tools and Tooling¶
Atlas data explorers feature
Driver¶
- Purpose of Driver and it's advantages
- Connect and Understand components of URI String
- CRUD syntax for chosen Driver
- Aggregation syntax for chosen Driver
Sample scenario will be same as CRUD
¶
Cursor, toArray
tokenization { "mappings": { "dynamic": false, "fields": { "name": [ { "type": "autocomplete", "tokenization": "edgeGram"} ] } }}
tokenization algorithms
MongoDB atlas search db.restaurants.aggregate([{ "$search": { "text": { "path": "name", "query": "cuban"} } }])
Atlas search index
All aggregation pipelines
getSiblingDB
upsert and other options
All CRUD operations, what every query return keep eye on that also
index in reverse, effects of index on search and sort, indexes on array
Pooling in nodejs, mongoclient
Syntax
Schema types and designs