MongoDB Architecture
Zones¶
- With the help of a shard key, MongoDB allows you to create zones of sharded data – also known as shard zones.
- You can associate each zone with one or more shards in the cluster.
- Similarly, A shard can associate with any number of zones.
- MongoDB migrates chunks covered by a zone only to those shards associated with the zone.
- MongoDB routes reads and writes that fall into a zone range only to those shards inside of the zone.
For GDPR and CCPA we can use this Zone based sharding of MongoDB for segmenting data by geographic area. Segmenting Data by Location
we will shard mongodb first in two regions one is in NA and another is in EU
The following diagram illustrates a sharded cluster that uses geographic zones to manage and satisfy GDPR and CCPA compliance.
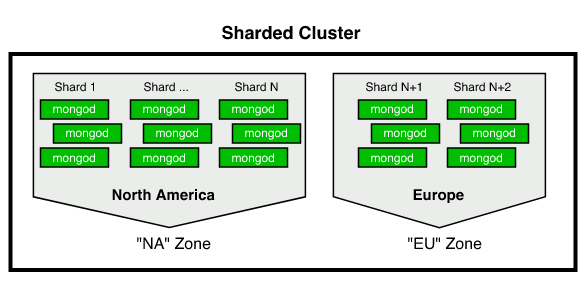
We require one zone per data center.
EU - European data center Shards deployed on this data center are assigned to the EU zone.
NA - North American data center Shards deployed on this data center are assigned to the NA zone.
Is defining ranges required in zones?
No, creating a zone range is not strictly required for zone-based sharding, but it can be useful for controlling how data is distributed across the shards.
Without zone ranges, MongoDB will still distribute the data across the shards based on the shard key values, but it may not distribute the data evenly across the zones. In some cases, this can result in one zone becoming overloaded with data while another zone has relatively little data.