What is Machine Learning?¶
Machine learning is a subfield of artificial intelligence, which is broadly defined as the capability of a machine to imitate intelligent human behavior. Artificial intelligence systems are used to perform complex tasks in a way that is similar to how humans solve problems.
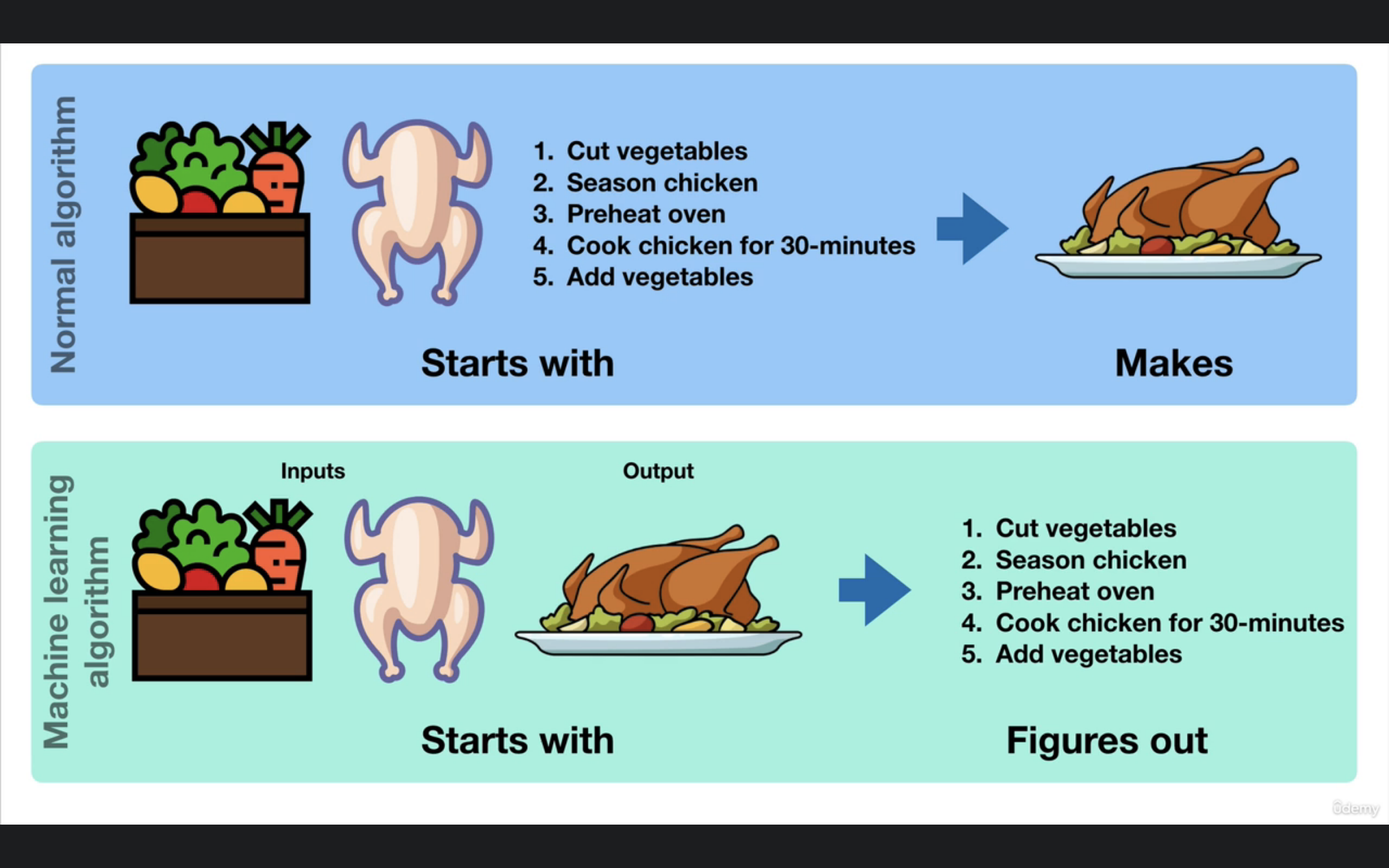
Machine learning algorithm starts with the input and output and try to fgure out the steps to acheive that output. It's based on the trial and error, ML will try this 1000 times to get the closets result.
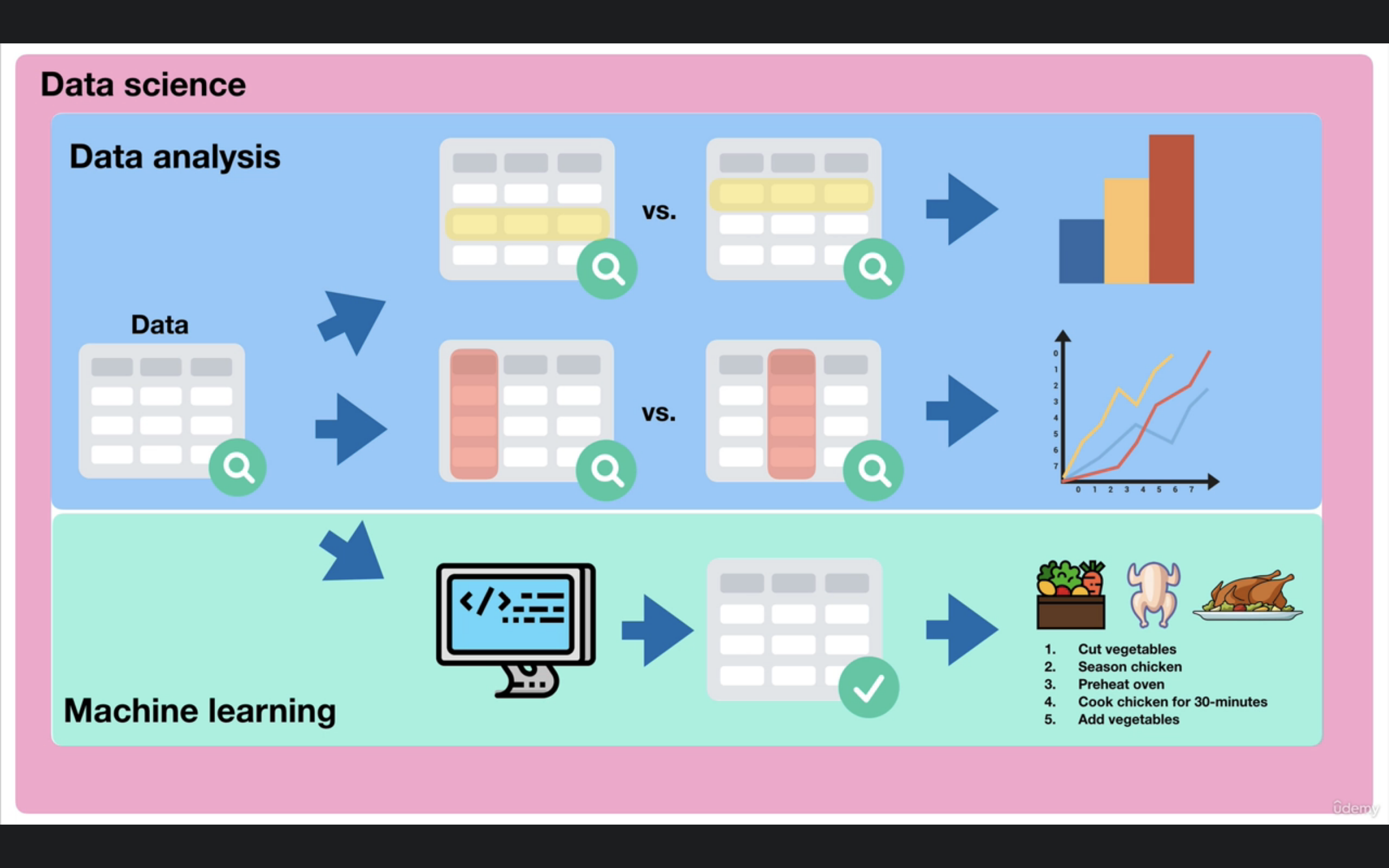
Data analysis is looking into the data we have, analysing it, visualising in terms of different graphs and plots. In other hand Data Science is get some actionable output out of this data.
Subtypes:
- Supervised
- classification
- regression
- Unsupervised
- clustering
- association rule learning
- Reinforcement
Supervised Learning¶
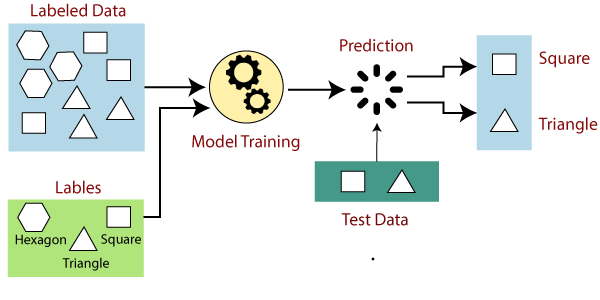
In this we use labelled data, a label data to train and test data to test the model
Supervised learning is the types of machine learning in which machines are trained using well "labelled" training data, and on basis of that data, machines predict the output. The labelled data means some input data is already tagged with the correct output.
In supervised learning, the training data provided to the machines work as the supervisor that teaches the machines to predict the output correctly. It applies the same concept as a student learns in the supervision of the teacher.
How Supervised Learning Works?¶
In supervised learning, models are trained using labelled dataset, where the model learns about each type of data. Once the training process is completed, the model is tested on the basis of test data (a subset of the training set), and then it predicts the output.
In the real-world, supervised learning can be used for Risk Assessment, Image classification, Fraud Detection, spam filtering, etc.
1. Classification¶
Classification algorithms are used when the output variable is categorical, which means there are two classes such as Yes-No, Male-Female, True-false, etc.
- Random Forest
- Decision Trees
- Logistic Regression
- Support vector Machines
Examples: - "Is this example one thing or another?" - Binary classification = two options - Multi-class classification = more than two options
2. Regression¶
Regression algorithms are used if there is a relationship between the input variable and the output variable. It is used for the prediction of continuous variables, such as Weather forecasting, Market Trends, etc. Below are some popular Regression algorithms which come under supervised learning:
- Linear Regression
- Regression Trees
- Non-Linear Regression
- Bayesian Linear Regression
- Polynomial Regression
Examples: - "How much will this house sell for?" - "How many people will buy this app?"
Unsupervised Learning¶
This is when data that doesn't have labels
unsupervised learning is a machine learning technique in which models are not supervised using training dataset. Instead, models itself find the hidden patterns and insights from the given data.
Unsupervised learning is much similar as a human learns to think by their own experiences, which makes it closer to the real AI.
Example: Suppose we have data of the customers order history, and now the marketing team want to send summer promotion eamils to customers but not everyone will be interested in summer clothes so now you run the unsupervised algorithm on this data and you noticed two groups, one who buys only on summer time and one who buys in winter time and you labeled them winter customers and summer customers and in this way we saved sending 1000s of unwanted emails.
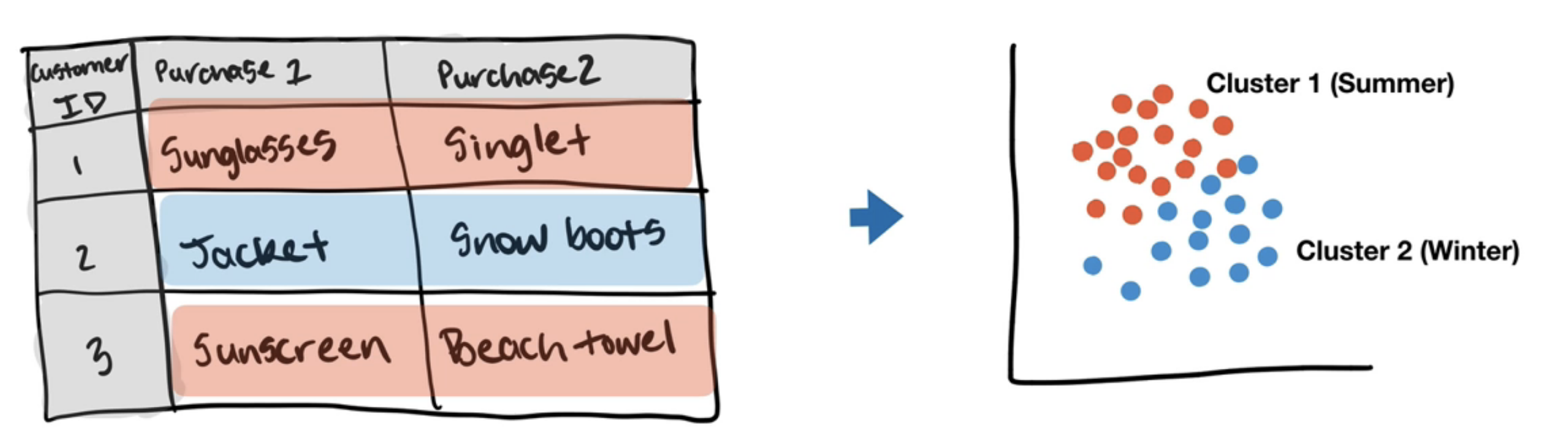
another example
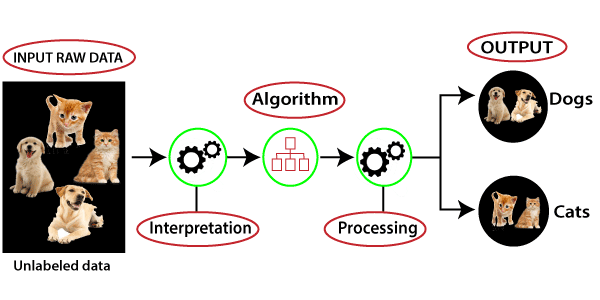
unsupervised learning algorithms:
- K-means clustering
- KNN (k-nearest neighbors)
- Hierarchal clustering
- Anomaly detection
- Neural Networks
- Principle Component Analysis
- Independent Component Analysis
- Apriori algorithm
- Singular value decomposition
Transfer Learning¶
training model on datasets requires processing power, and if the dataset is huge with billions of data then it will require huge processing power and also lot's of time. If we have one model which is already trained on one perticular case then instead of retraining we can use that model agin and train only for other cases.
Transfer learning is the reuse of a pre-trained model on a new problem. In transfer learning, the knowledge of an already trained machine learning model is applied to a different but related problem. For example, if you trained a simple classifier to predict whether an image contains a backpack, you could use the knowledge that the model gained during its training to recognize other objects like sunglasses.
Reinforcement Learning¶
Teaching machine based on trial and error through rewards and punishments
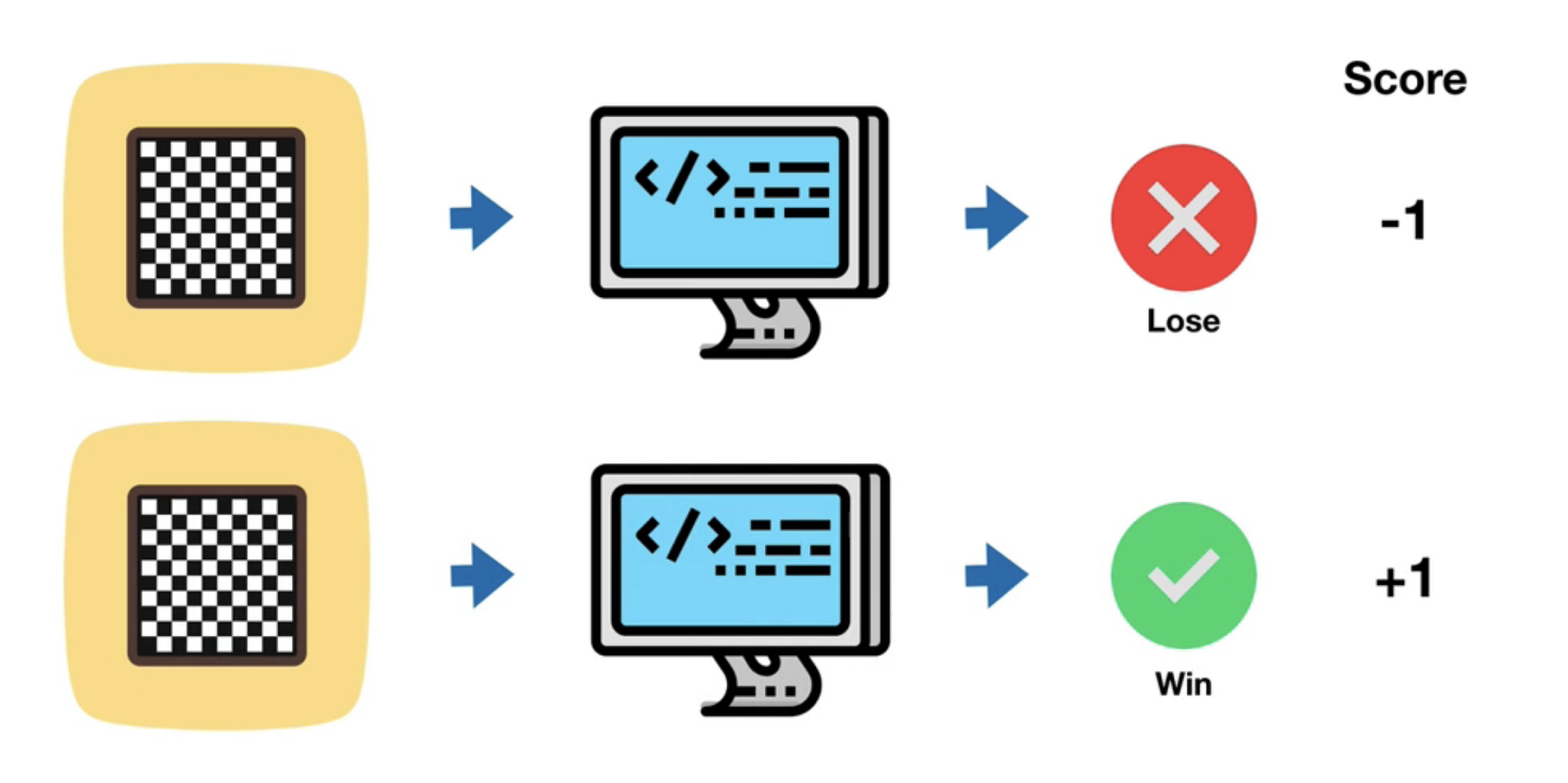
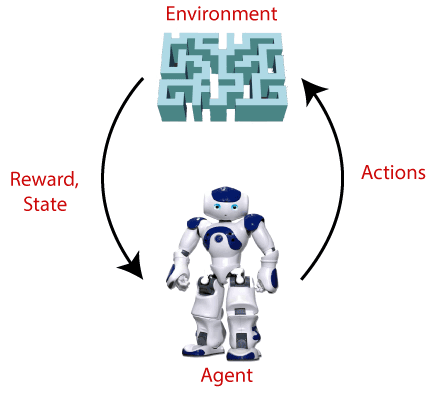
Reinforcement Learning is a feedback-based Machine learning technique in which an agent learns to behave in an environment by performing the actions and seeing the results of actions. For each good action, the agent gets reward, and for each bad action, the agent gets penalty.
The good example of this is training machin to play the chess.
In Reinforcement Learning, the agent learns automatically using feedbacks without any labeled data, unlike supervised learning.
Since there is no labeled data, so the agent is bound to learn by its experience only.
Types of Data¶
-
Structured Structured data is in the form of csv, excel or sql data which follows structure.
-
Unstructured Unstructured data includes images, video, audio, eamils etc. which actually doesn’t have any structure we can convert this into numbers and structure them but the image of one dog is different with another dog.
Above data contains sub data types - Static data that doesn't change over time example - heart disease patient data - Streaming data that constantly change over time example - predict stock price based on news headlines which changes constantly.
💡
The more data the better
Tip
Check this Framework of Machine Learning
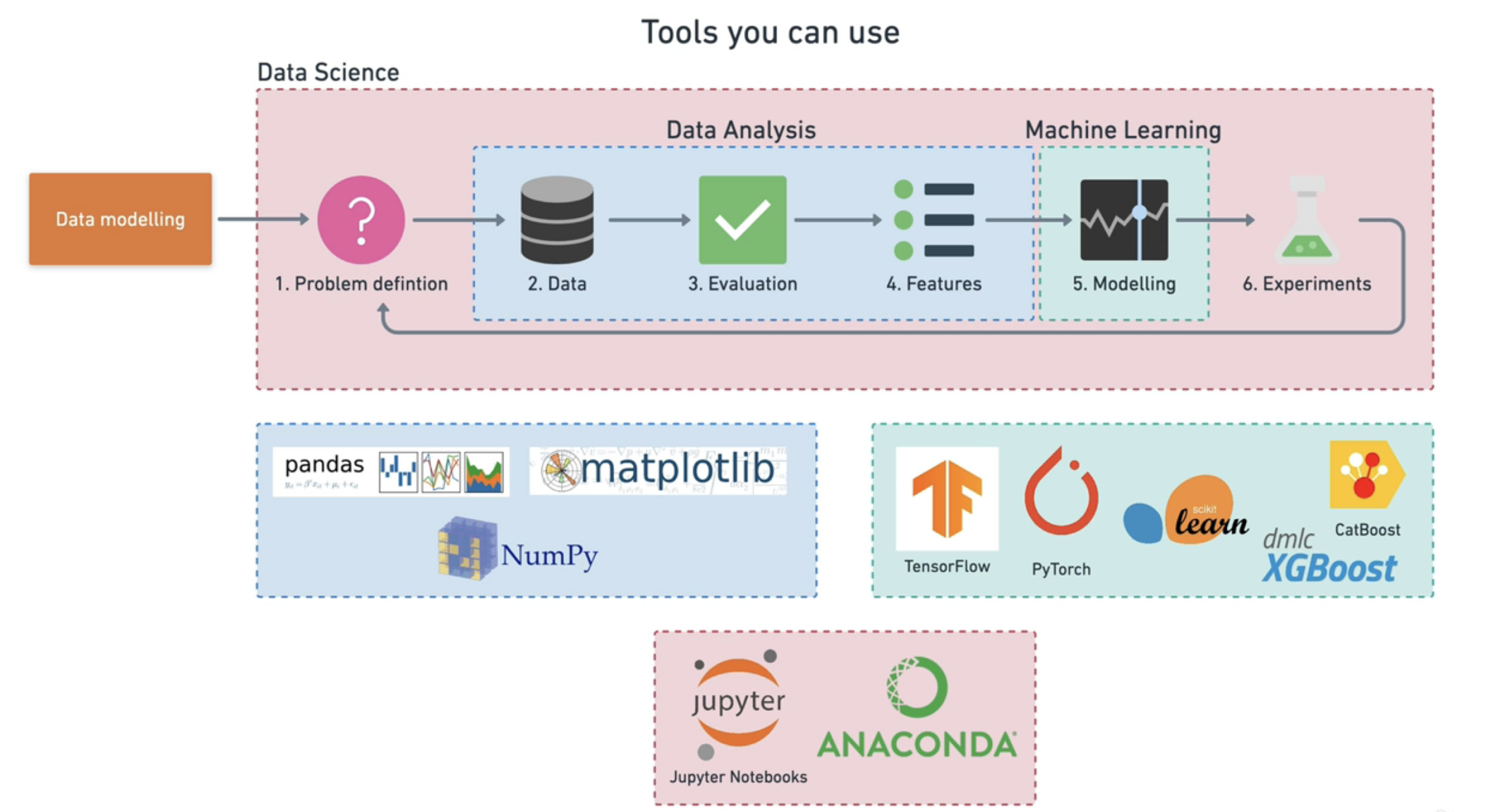
Tools for Machine Learning and Data Science¶
- Anaconda
- Jupyter Notebook
- Pandas
- Numpy
- Matplotlib
- TensorFlow
- PyTorch
- scikit Learn
- CatBoost
- dmlc XGBoost